
Figure 1 Collector current comparison circuit.
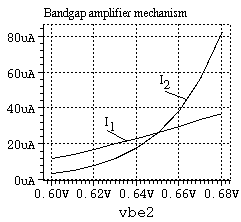
Figure 2 The current, I1, is greater
than the current I2 at low Vbe2.
 Figure 1 Collector current comparison circuit.
|
Ic = n IseVbe/VTwhere n is the emitter area multiplication factor.
At low currents the Vbes of the two transistors are nearly equal, because the drop across R is small, and I1 is greater than I2 because N1 is bigger. As the base voltage increases, currents increase. The current in N1 is limited by R to increase linearly, while the current in N2 increases exponentially with Vbe2.
There is an input voltage at which the currents are equal(about 0.65V in this simulation). If Vbe2 increases above that value, I2 > I1. If it drops below it, I2 < I1.